Hybrid solar inverter systems now serve as a central element in today’s solar energy arrangements. With rising energy prices and decreasing grid reliability across numerous areas, people seek solutions that manage solar panels, storage units, and utility supply simultaneously. This is precisely why hybrid inverters excel. Beyond simply transforming DC into AC, they direct energy distribution, shield devices, and maintain continuous power during varying circumstances.
Firms such as Soonest Power emphasize developing hybrid inverter products that function effectively in practical scenarios, spanning modest residences to extensive business and factory installations. Their offerings include both single-phase and three-phase variants, and Soonest hybrid inverters prioritize adaptability, consistent performance, and extended operational duration.

What Is a Hybrid Solar Inverter System and How Does It Work?
Prior to selecting an arrangement, grasping the distinctions of a hybrid inverter from conventional grid-tied or isolated inverters proves beneficial. The primary variation involves the quantity of energy sources it processes and the seamless manner in which it transitions among them.
Integrated Solar, Grid, and Battery Power Conversion
A hybrid inverter links solar arrays, battery reserves, and the main grid within a single framework. Depending on configuration preferences, it routes solar output directly to appliances, preserves surplus in storage, or supplies excess to the network.
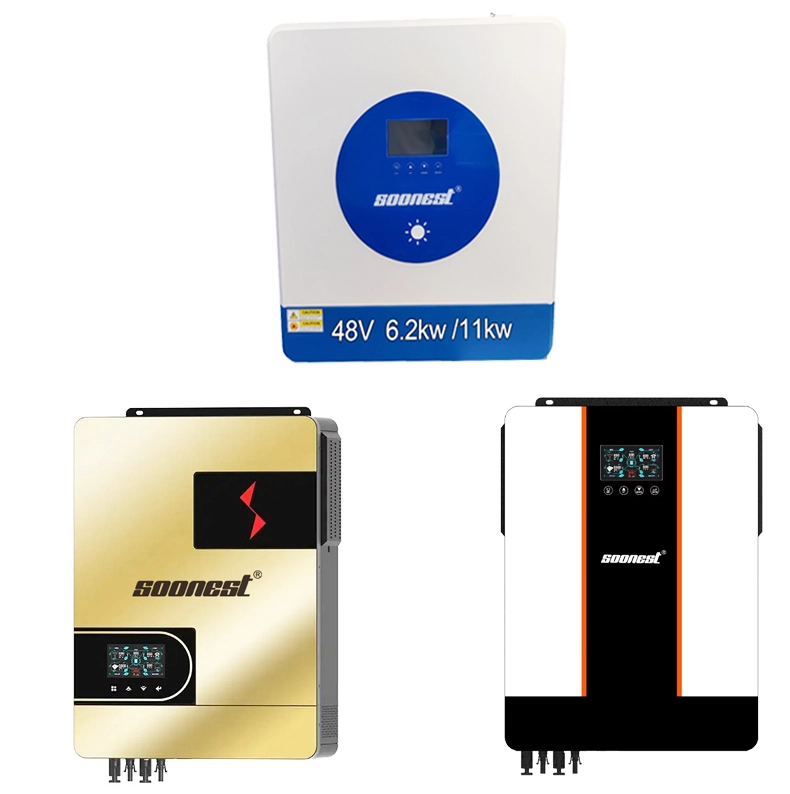
This unified approach minimizes reliance on additional components, such as standalone regulators or relay mechanisms. For example, within units like the SOONEST MY Series and SF Series hybrid inverters, solar, storage, and grid connections integrate into one streamlined enclosure, thereby easing deployment and streamlining electrical connections.
Smart Energy Flow Control in Real Time
Contemporary hybrid inverters employ embedded algorithms to determine energy pathways instantaneously. Thus, during peak solar generation, appliances receive direct supply, and when illumination diminishes, reserves or the network activate without interruption.
Soonest hybrid inverters incorporate MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) methods to sustain solar arrays at optimal yield levels, irrespective of fluctuating illumination. Consequently, such capability curbs energy loss from panels amid overcast conditions or initial daylight periods.
Stable AC Output for Residential and Commercial Loads
Energy purity holds significance, particularly for devices including motors, computing units, and delicate circuitry. Soonest hybrid inverters generate pure sine wave AC output that aligns closely with utility standards, which in turn diminishes interference, thermal buildup, and progressive deterioration of linked apparatus.
Which Core Components Define a Hybrid Solar Inverter System?
Each hybrid inverter houses an array of physical elements and regulatory mechanisms that collaborate seamlessly, ultimately determining the framework’s endurance over extended periods.
High-Efficiency MPPT Solar Charge Controllers
MPPT regulators modify voltage and amperage to draw maximum practical output from solar arrays. Per insights from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), these MPPT configurations produce 20–30% more energy relative to elementary PWM variants amid variable lighting scenarios.
Soonest hybrid inverters feature expansive MPPT voltage tolerances, enabling compatibility with varied array configurations and series lengths, which benefits both rooftop domestic setups and substantial terrestrial installations alike.
Advanced Power Conversion and Protection Circuits
Safeguard elements remain indispensable for sustained solar frameworks, since excesses in voltage, circuit faults, thermal overloads, and inverted polarities pose risks to connected hardware.
Soonest hybrid inverters embed essential defenses including:
- Overload and short-circuit protection
- Battery reverse connection protection
- Over-temperature shutdown
These mechanisms ensure frameworks maintain equilibrium in elevated temperatures and amid abrupt demand fluctuations.
Intelligent Monitoring and Communication Interfaces
Distant oversight has evolved into a baseline expectation within the solar sector, where individuals anticipate accessing operational details without accessing the inverter enclosure directly.
Soonest hybrid inverters accommodate connectivity protocols like RS485 and WiFi, thereby permitting operators and technicians to observe generation levels, reserve conditions, and diagnostic alerts via digital interfaces.
How Do Single-Phase and Three-Phase Hybrid Inverters Differ?
Selecting single-phase versus three-phase configurations relies on demand magnitude, usage category, and regional utility guidelines.
Single-Phase Power for Homes and Small Businesses
Single-phase hybrid inverters prevail in domestic frameworks and minor retail spaces, as they deploy more easily and conform to standard residential circuits.
The SOONEST MY Series Hybrid Inverter (1kW–10.2kW) and SOONEST SF Series Hybrid Inverter (1kW–10.2kW) target such contexts. They facilitate reserve capacity, auxiliary supply, and everyday solar utilization without excess intricacy.
Three-Phase Output for Industrial and Commercial Systems
Production facilities, agricultural operations, corporate structures, and fabrication areas commonly depend on three-phase delivery for substantial machinery and equilibrated demands.
The SOONEST IP65 High Voltage 3-Phase Hybrid Inverter (10kW–50kW, 380V) accommodates these settings. It delivers elevated generation, robust demand management, and dependable function beneath persistent utilization.
Scalability for Growing Energy Demands
As requirements for power escalate, inverter limits often constrain advancement, yet three-phase frameworks permit simpler augmentation and superior demand allocation, rendering them prevalent in enterprise solar initiatives.
Table 1: Single-Phase vs Three-Phase Hybrid Inverters (Industry Comparison)
| Feature | Single-Phase Hybrid Inverter | Three-Phase Hybrid Inverter |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Application | Homes, small offices | Factories, commercial sites |
| Voltage Standard | 220–240V | 380–415V |
| Load Capacity | Light to medium | Medium to heavy |
| Wiring Complexity | Lower | Higher |
| System Scalability | Limited | Strong |
Why Is Environmental Protection and Durability So Important?
Hybrid inverters routinely function in external environments or partially exposed utility areas, where resilience to surroundings profoundly influences lifespan and ongoing expenses.
IP65 Protection for Harsh Outdoor Conditions
IP classifications outline resistance levels to particulates and moisture. IP65, as defined by IEC criteria, provides total particulate sealing and endurance against directed streams from every orientation.
The SOONEST IP65 three-phase hybrid inverter series accommodates external deployment absent supplementary housings, proving particularly advantageous in locales marked by elevated moisture, particulates, or recurrent precipitation.
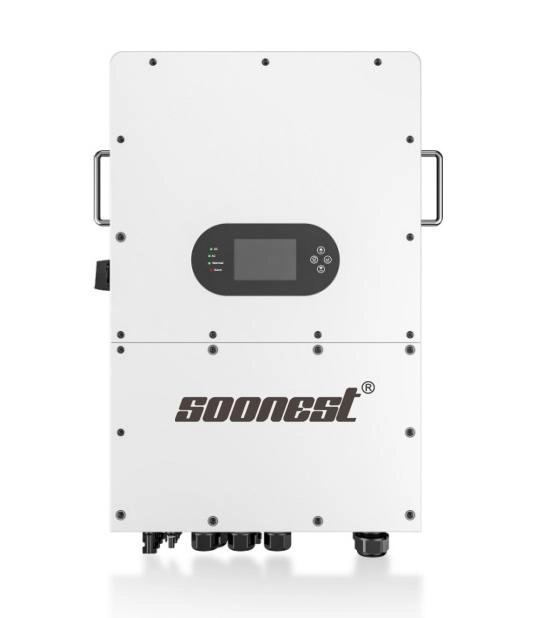

Wide Operating Temperature and Voltage Ranges
Across various solar territories, surrounding heat frequently surpasses 45°C, necessitating that inverters manage thermal stress without premature capacity reduction.
Soonest hybrid inverters adapt to broad thermal scopes, thereby aiding frameworks to sustain steadiness in arid expanses, littoral zones, and equatorial settings.
Long-Term Reliability for Continuous Operation
Assurance derives from both material quality and validation processes, as enterprise hybrid inverters generally endure durability evaluations and cycle testing before distribution, which mitigates premature malfunctions and enhances prolonged framework consistency.
Which Soonest Hybrid Inverter Is Right for Different Applications?
Diverse operators pursue varied energy objectives, and Soonest furnishes an assortment of hybrid inverter lines tailored to authentic operational contexts.
MY Series for Flexible Residential and Backup Power Systems
The SOONEST MY Series Hybrid Inverter (1kW–10.2kW single phase) aligns with households desiring autonomous solar consumption alongside reserve capability. It performs effectively in expansive dwellings, multi-unit residences, and compact workspaces where enclosure and circuit straightforwardness hold value.
SF Series for Smart Energy Management and Remote Monitoring
The SOONEST SF Series Hybrid Inverter (1kW–10.2kW single phase) centers on intelligent regulation and surveillance. It accommodates those seeking transparent operational insights, versatile reserve application, and reliable everyday performance.
IP65 Three-Phase Series for Commercial and Industrial Power Systems
Regarding substantial endeavors, the SOONEST IP65 10kW–50kW High Voltage 3-Phase Hybrid Inverter upholds rigorous demands and exterior placement. It sees broad adoption in enterprise edifices, rural enterprises, and manufacturing locales.
Table 2: Soonest Hybrid Inverter Product Overview
| Series | Phase Type | Power Range | Protection Level | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MY Series | Single Phase | 1kW–10.2kW | IP20 | Residential, backup |
| SF Series | Single Phase | 1kW–10.2kW | IP20 | Smart home systems |
| IP65 Series | Three Phase | 10kW–50kW | IP65 | Commercial, industrial |
FAQ
Q1: Can a hybrid solar inverter work without batteries?
A: Yes. Most hybrid inverters, including Soonest models, can operate in grid-connected mode without batteries. Batteries can be added later if backup or energy storage is needed.
Q2: Is a three-phase hybrid inverter necessary for small homes?
A: Usually not. Small homes typically use single-phase power. Three-phase hybrid inverters are better suited for larger loads or commercial equipment.
Q3: How long does a hybrid solar inverter typically last?
A: With proper installation and ventilation, quality hybrid inverters often operate for 8–12 years or longer. Environmental conditions and load patterns play a big role in actual lifespan.